Exs. coin flip is a head: λ=.5 die roll is a 6: λ=.166666 next digit of normal number is d: λ=.1 card is suit s: λ=.25
Probability of non-occurence decreases exponentially with time.
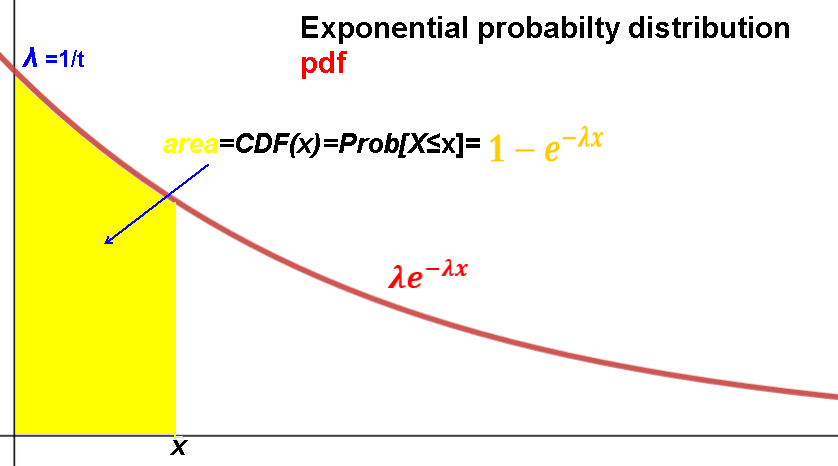
pdf(x)= λe-λx
Probability that the event happens in no more than (i.e. within) x amount of time or
the probability that there is at least 1 thing in x area/space units:
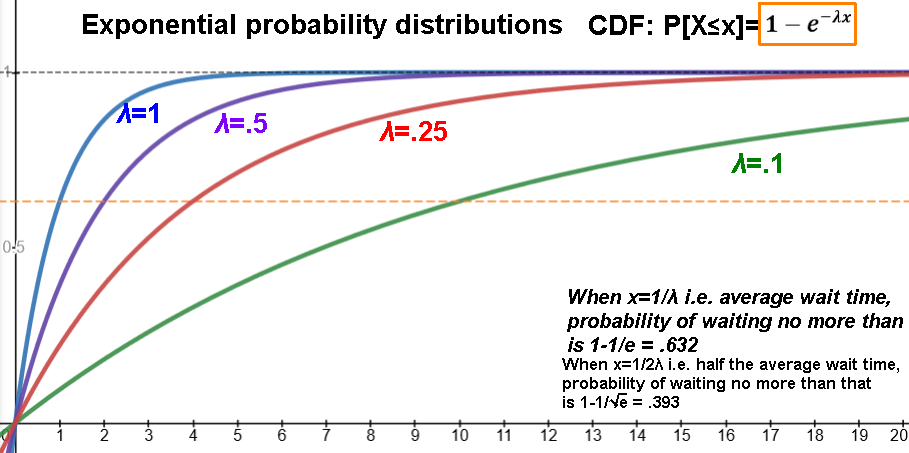
CDF(x) = P[X≤x] = 1-e-λx
Probability that the event happens in at least (i.e. after) x amount of time:
1-CDF(x)=P[X>x]= e-λx
Given a probability percentile 0≤p≤1, what is the time x: Quantile InverseCDF Q(p)= -ln(1-p) / λ

The probability of waiting no more than the
average wait time (x≤1/λ) is 1-1/e ≈ .632
The probability of waiting more than the
average wait time (x>1/λ) is 1/e ≈ .3679
The probability of waiting no more than
half the average wait time (x≤1/(2λ) is 1-1/√e ≈ .393
The probability of waiting between
half the average wait time and the average waiting time is 1/√e-1/e ≈ .238
The probability of waiting no more than
twice the average wait time (x≤2/λ) is 1-1/e2 ≈ .864
The probability of waiting more than
twice the average wait time (x>2/λ) is 1/e2 ≈ .135